Intel VT-x operations
Detect VMX Support
#virtualmachineextension #vmx
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
//23.6 DISCOVERING SUPPORT FOR VMX
bool
DetectVmxSupport()
{
bool VMX = false;
__asm {
XOR EAX, EAX
INC EAX
CPUID
BT ECX, 0x5
JC VMXSupport
VMXNotSupport :
JMP NopInstr
VMXSupport :
MOV VMX, 0x1
NopInstr :
NOP
}
return VMX;
}
|
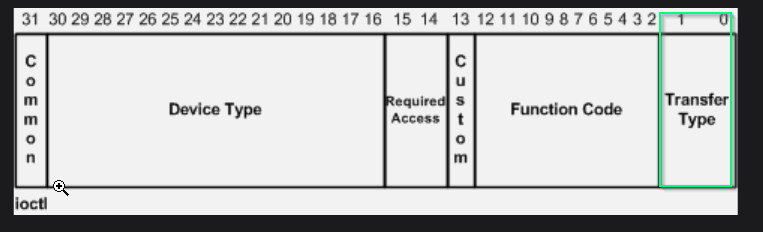
User-mode Buffer To Kernel-mode
- METHOD_BUFFERED -
Irp->AssociatedIrp.SystemBuffer
- METHOD_IN_DIRECT and METHOD_OUT_DIRECT -
Irp->AssociatedIrp.SystemBuffer , the I/O manager is in charge of allocating a system buffer and set the irp->associatedirp.systembuffer and copies the content of user input buffer into the System Buffer.
- METHOD_NIETHER -
Parameters.DeviceIoControl.Type3InputBuffer
- in
IO_STACK_LOCATION . Output buffer -> Irp->UserBuffer.
- Buffer size
Parameters.DeviceIoControl.InputBufferLength and Parameters.DeviceIoControl.OutputBufferLength
- Accessing the buffer goes
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| InBuf = IrpStack->Parameters.DeviceIoControl.Type3InputBuffer;
OutBuf = Irp->UserBuffer;
try
{
ProbeForRead(InBuf, InBufLength, sizeof(UCHAR));
}
except(EXCEPTION_EXECUTE_HANDLER)
{
NtStatus = GetExceptionCode();
DbgPrint(
"Exception while accessing InBuf 0X%08X in METHOD_NEITHER\n",
NtStatus);
break;
}
Mdl = IoAllocateMdl(InBuf, InBufLength, FALSE, TRUE, NULL);
try
{
MmProbeAndLockPages(Mdl, UserMode, IoReadAccess);
}
except(EXCEPTION_EXECUTE_HANDLER)
{
NtStatus = GetExceptionCode();
DbgPrint((
"Exception while locking InBuf 0X%08X in METHOD_NEITHER\n",
NtStatus));
IoFreeMdl(Mdl);
break;
}
//map the address to system space and read it
Buffer = MmGetSystemAddressForMdlSafe(Mdl, NormalPagePriority | MdlMappingNoExecute);
//after reading, unlock and unmap
MmUnlockPages(Mdl);
IoFreeMdl(Mdl);
|
1
2
3
4
| #define IOCTL_Device_Function CTL_CODE(DeviceType, Function, Method, Access)
#define IOCTL_TEST \
CTL_CODE(FILE_DEVICE_UNKNOWN, 0x801, METHOD_BUFFERED, FILE_ANY_ACCESS)
|
Creating Custom Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM)
CPU Execution Mode
The result of the great great first-generation Intel VT-x
- Allowing VMM to run in a new root mode below ring 0.
- All sensitive calls are trapped automatically to the hypervisor.
- Storing Guest in VMCS (Intel VT-x)
#vmm
- There should be equal numbers of VMCSs and VMXON regions as the number of logical processors.
- Check if VMX operations are supported
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| BOOLEAN
IsVmxSupported()
{
CPUID Data = {0};
//
// Check for the VMX bit
//
__cpuid((int *)&Data, 1);
if ((Data.ecx & (1 << 5)) == 0)
return FALSE;
IA32_FEATURE_CONTROL_MSR Control = {0};
Control.All = __readmsr(MSR_IA32_FEATURE_CONTROL);
//
// BIOS lock check
//
if (Control.Fields.Lock == 0)
{
Control.Fields.Lock = TRUE;
Control.Fields.EnableVmxon = TRUE;
__writemsr(MSR_IA32_FEATURE_CONTROL, Control.All);
}
else if (Control.Fields.EnableVmxon == FALSE)
{
DbgPrint("[*] VMX locked off in BIOS");
return FALSE;
}
return TRUE;
}
|
- Allocating VMCS and VMXON regions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| typedef struct _VIRTUAL_MACHINE_STATE
{
UINT64 VmxonRegion; // VMXON region
UINT64 VmcsRegion; // VMCS region
} VIRTUAL_MACHINE_STATE, *PVIRTUAL_MACHINE_STATE;
VIRTUAL_MACHINE_STATE * g_GuestState;
BOOLEAN
InitializeVmx()
{
if (!IsVmxSupported())
{
DbgPrint("[*] VMX is not supported in this machine !");
return FALSE;
}
ProcessorCounts = KeQueryActiveProcessorCount(0);
g_GuestState = ExAllocatePoolWithTag(NonPagedPool,
sizeof(VIRTUAL_MACHINE_STATE) * ProcessorCounts,
POOLTAG);
KAFFINITY AffinityMask;
for (size_t i = 0; i < ProcessorCounts; i++)
{
AffinityMask = MathPower(2, i);
DbgPrint("AffinityMask %lx", AffinityMask);
KeSetSystemAffinityThread(AffinityMask);
DbgPrint("\t\tCurrent thread is executing in %d th logical processor.", i);
AsmEnableVmxOperation();
/*
AsmEnableVmxOperation PROC PUBLIC
PUSH RAX ; Save the state
XOR RAX, RAX ; Clear the RAX
MOV RAX, CR4
OR RAX,02000h ; Set the 14th bit
MOV CR4, RAX
POP RAX ; Restore the state
RET
AsmEnableVmxOperation ENDP
*/
DbgPrint("[*] VMX Operation Enabled Successfully !");
//Allocating contiguous memory for VMCS and VMXON, https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/drivers/ddi/content/wdm/ne-wdm-_memory_caching_type
// AllocateVmxonRegion(&g_GuestState[i]);
// AllocateVmcsRegion(&g_GuestState[i]);
}
return TRUE;
}
|
CR0.PE, CR0.NE, CR0.PG, and CR4.VMXE bit should be 1 to be executed in page-protected mode- Writing the
Revision Identifier from IA32_VMX_BASIC_MSR to VMXON Region
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
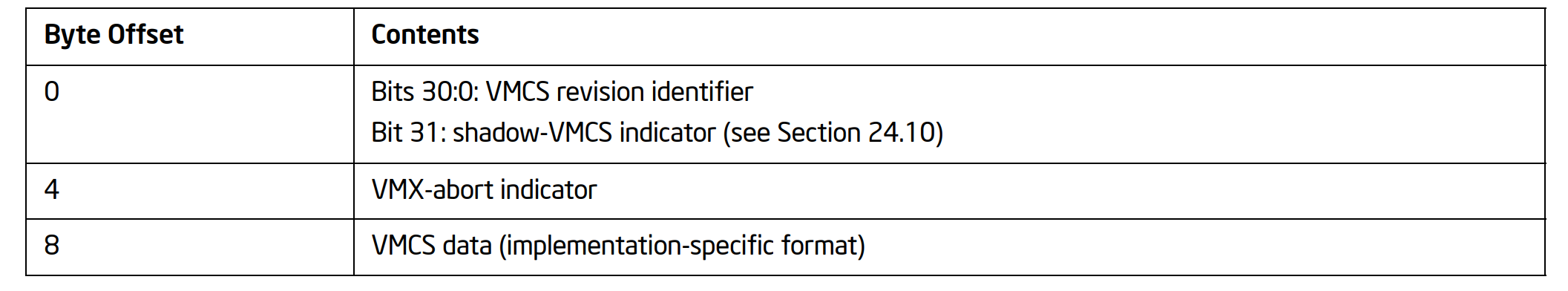
| typedef union _IA32_VMX_BASIC_MSR
{
ULONG64 All;
struct
{
ULONG32 RevisionIdentifier : 31; // [0-30]
ULONG32 Reserved1 : 1; // [31]
ULONG32 RegionSize : 12; // [32-43]
ULONG32 RegionClear : 1; // [44]
ULONG32 Reserved2 : 3; // [45-47]
ULONG32 SupportedIA64 : 1; // [48]
ULONG32 SupportedDualMoniter : 1; // [49]
ULONG32 MemoryType : 4; // [50-53]
ULONG32 VmExitReport : 1; // [54]
ULONG32 VmxCapabilityHint : 1; // [55]
ULONG32 Reserved3 : 8; // [56-63]
} Fields;
} IA32_VMX_BASIC_MSR, *PIA32_VMX_BASIC_MSR;
IA32_VMX_BASIC_MSR basic = {0};
basic.All = __readmsr(MSR_IA32_VMX_BASIC);
DbgPrint("[*] MSR_IA32_VMX_BASIC (MSR 0x480) Revision Identifier %llx", basic.Fields.RevisionIdentifier);
// Changing Revision Identifier
*(UINT64 *)AlignedVirtualBuffer = basic.Fields.RevisionIdentifier;
|
AllocateVmxonRegion , writes the IA32_VMX_BASIC_MSR.Fields.RevisionIdentifier to VMXON region and turn VMXON
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| BOOLEAN
AllocateVmxonRegion(IN VIRTUAL_MACHINE_STATE * GuestState)
{
// at IRQL > DISPATCH_LEVEL memory allocation routines don't work
if (KeGetCurrentIrql() > DISPATCH_LEVEL)
KeRaiseIrqlToDpcLevel();
PHYSICAL_ADDRESS PhysicalMax = {0};
PhysicalMax.QuadPart = MAXULONG64;
int VMXONSize = 2 * VMXON_SIZE;
BYTE * Buffer = MmAllocateContiguousMemory(VMXONSize + ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE, PhysicalMax); // Allocating a 4-KByte Contigous Memory region
PHYSICAL_ADDRESS Highest = {0}, Lowest = {0};
Highest.QuadPart = ~0;
// BYTE* Buffer = MmAllocateContiguousMemorySpecifyCache(VMXONSize + ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE, Lowest, Highest, Lowest, MmNonCached);
if (Buffer == NULL)
{
DbgPrint("[*] Error : Couldn't Allocate Buffer for VMXON Region.");
return FALSE; // ntStatus = STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES;
}
UINT64 PhysicalBuffer = VirtualToPhysicalAddress(Buffer);
// zero-out memory
RtlSecureZeroMemory(Buffer, VMXONSize + ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE);
UINT64 AlignedPhysicalBuffer = (BYTE *)((ULONG_PTR)(PhysicalBuffer + ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE - 1) & ~(ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE - 1));
UINT64 AlignedVirtualBuffer = (BYTE *)((ULONG_PTR)(Buffer + ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE - 1) & ~(ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE - 1));
DbgPrint("[*] Virtual allocated buffer for VMXON at %llx", Buffer);
DbgPrint("[*] Virtual aligned allocated buffer for VMXON at %llx", AlignedVirtualBuffer);
DbgPrint("[*] Aligned physical buffer allocated for VMXON at %llx", AlignedPhysicalBuffer);
// get IA32_VMX_BASIC_MSR RevisionId
IA32_VMX_BASIC_MSR basic = {0};
basic.All = __readmsr(MSR_IA32_VMX_BASIC);
DbgPrint("[*] MSR_IA32_VMX_BASIC (MSR 0x480) Revision Identifier %llx", basic.Fields.RevisionIdentifier);
// Changing Revision Identifier
*(UINT64 *)AlignedVirtualBuffer = basic.Fields.RevisionIdentifier;
int Status = __vmx_on(&AlignedPhysicalBuffer);
if (Status)
{
DbgPrint("[*] VMXON failed with status %d\n", Status);
return FALSE;
}
g_GuestState->VmxonRegion = AlignedPhysicalBuffer;
return TRUE;
}
|
AllocateVmxonRegion , writes the IA32_VMX_BASIC_MSR.Fields.RevisionIdentifier to VMCS region and VMPTRLD sets the current VMCS on a logical processor.
vmptrst(PA) sets the current VMCS at the specified PA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| BOOLEAN
AllocateVmcsRegion(IN VIRTUAL_MACHINE_STATE * GuestState)
{
//
// at IRQL > DISPATCH_LEVEL memory allocation routines don't work
//
if (KeGetCurrentIrql() > DISPATCH_LEVEL)
KeRaiseIrqlToDpcLevel();
PHYSICAL_ADDRESS PhysicalMax = {0};
PhysicalMax.QuadPart = MAXULONG64;
int VMCSSize = 2 * VMCS_SIZE;
BYTE * Buffer = MmAllocateContiguousMemory(VMCSSize + ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE, PhysicalMax); // Allocating a 4-KByte Contigous Memory region
PHYSICAL_ADDRESS Highest = {0}, Lowest = {0};
Highest.QuadPart = ~0;
// BYTE* Buffer = MmAllocateContiguousMemorySpecifyCache(VMXONSize + ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE, Lowest, Highest, Lowest, MmNonCached);
UINT64 PhysicalBuffer = VirtualToPhysicalAddress(Buffer);
if (Buffer == NULL)
{
DbgPrint("[*] Error : Couldn't Allocate Buffer for VMCS Region.");
return FALSE; // ntStatus = STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES;
}
// zero-out memory
RtlSecureZeroMemory(Buffer, VMCSSize + ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE);
UINT64 AlignedPhysicalBuffer = (BYTE *)((ULONG_PTR)(PhysicalBuffer + ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE - 1) & ~(ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE - 1));
UINT64 AlignedVirtualBuffer = (BYTE *)((ULONG_PTR)(Buffer + ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE - 1) & ~(ALIGNMENT_PAGE_SIZE - 1));
DbgPrint("[*] Virtual allocated buffer for VMCS at %llx", Buffer);
DbgPrint("[*] Virtual aligned allocated buffer for VMCS at %llx", AlignedVirtualBuffer);
DbgPrint("[*] Aligned physical buffer allocated for VMCS at %llx", AlignedPhysicalBuffer);
// get IA32_VMX_BASIC_MSR RevisionId
IA32_VMX_BASIC_MSR basic = {0};
basic.All = __readmsr(MSR_IA32_VMX_BASIC);
DbgPrint("[*] MSR_IA32_VMX_BASIC (MSR 0x480) Revision Identifier %llx", basic.Fields.RevisionIdentifier);
// Changing Revision Identifier
*(UINT64 *)AlignedVirtualBuffer = basic.Fields.RevisionIdentifier;
int Status = __vmx_vmptrld(&AlignedPhysicalBuffer);
if (Status)
{
DbgPrint("[*] VMCS failed with status %d\n", Status);
return FALSE;
}
g_GuestState->VmcsRegion = AlignedPhysicalBuffer;
return TRUE;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| VOID
TerminateVmx()
{
DbgPrint("\n[*] Terminating VMX...\n");
KAFFINITY AffinityMask;
for (size_t i = 0; i < ProcessorCounts; i++)
{
AffinityMask = MathPower(2, i);
KeSetSystemAffinityThread(AffinityMask);
DbgPrint("\t\tCurrent thread is executing in %d th logical processor.", i);
__vmx_off();
MmFreeContiguousMemory(PhysicalToVirtualAddress(g_GuestState[i].VmxonRegion));
MmFreeContiguousMemory(PhysicalToVirtualAddress(g_GuestState[i].VmcsRegion));
}
DbgPrint("[*] VMX Operation turned off successfully. \n");
}
|
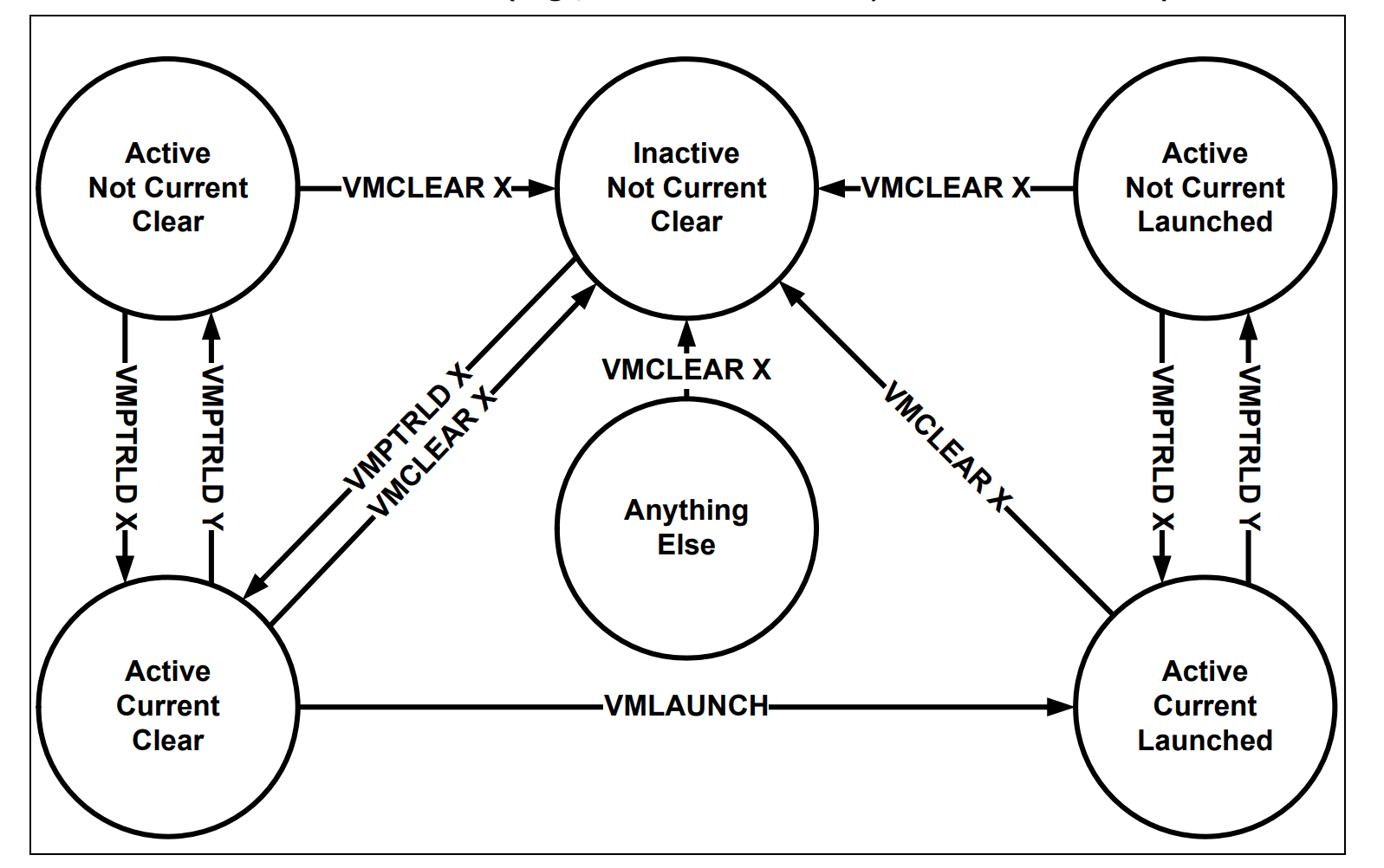
VMCS
Active vs. Current
- There might be several VMCSs simultaneously in a processor, but just one of them is currently active
VMCLEAR, VMPTRLD, VMREAD, and VMWRITE instructions.
- VMLAUNCH, VMREAD, VMRESUME, and VMWRITE instructions operate only on the current VMCS
- VMLAUNCH can only execute if the VMCS is cleared
- VMCLEAR can only execute on VMCS that’s launched.
Extended Page Table (EPT)
The result of the great second-generation Intel VT-X
History of Software MMU And Why
Intel EPT Evaluation
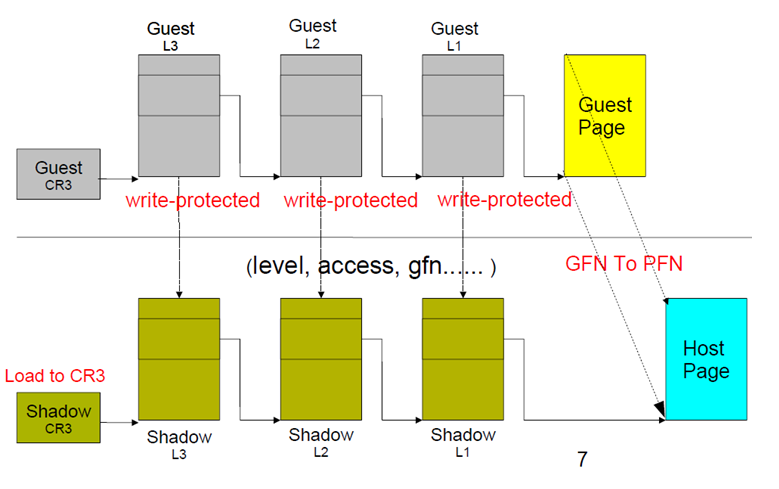
- Software MMU is needed to help facilitate virtual machine memory access
- Works by keeping shadow page table cohernt to the Guest OS page table
- Many many traps as there are many memory access happening all the time in the Guest OS.
- GVA - page table -> GPA -> SoftwareMMU -> shadow page table lookup -> PA
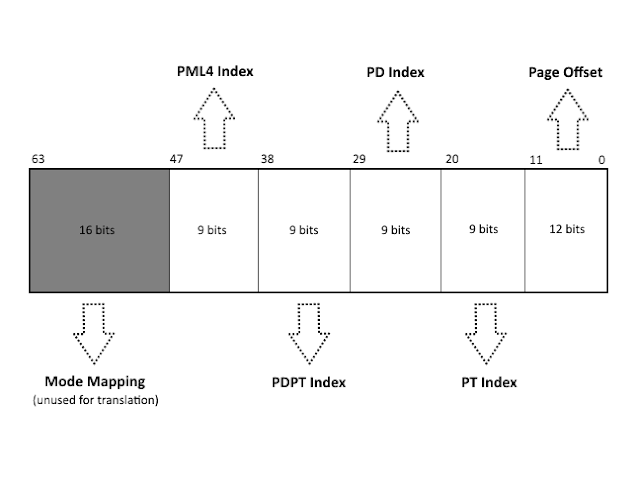
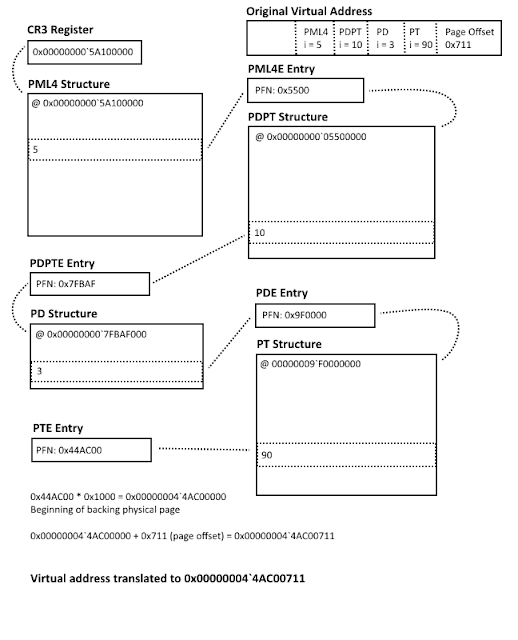
Review 4-Level Paging
- Virtual address breaks into 6 parts. only 5 parts are used to determine the physical address
- PML4 Index determines the index inside of the PML4 table
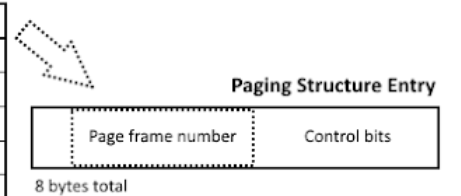
- After finding the entry in the PML4 table, look for Paging Structure Entry and its Page Frame Number (PFN)
- Multiply
0x1000 by the PFN to find the corresponding Page Directory Pointer Table (PDPT)
- Use the Page frame number to locate the entry inside of Page Directory Pointer Table and use PDPT Index from virtual address to locate the index of pointer inside of PDPT
- If the entry has
ULONG64 PageSize : 1; set to 1, then it can map to 1 GB page, otherwise 2MB
- Look for PGN again, multiply by
0x1000
- Now we arrives at Page Directory (PD), using PD Index to locate the PD entry
- find PFN again, multiply by
0x1000
- Arrive at Page Table (PT), using PT Index to locate the PT Entry
- Use PFN again, to find the actual physical page
- Applying the PT Offset, to findw the exact location of the virtual memory inside of physical memory
Shadow Page Tables (Legacy)
- Software-assisted paging
- VMM maintains the Shadow Page Tables
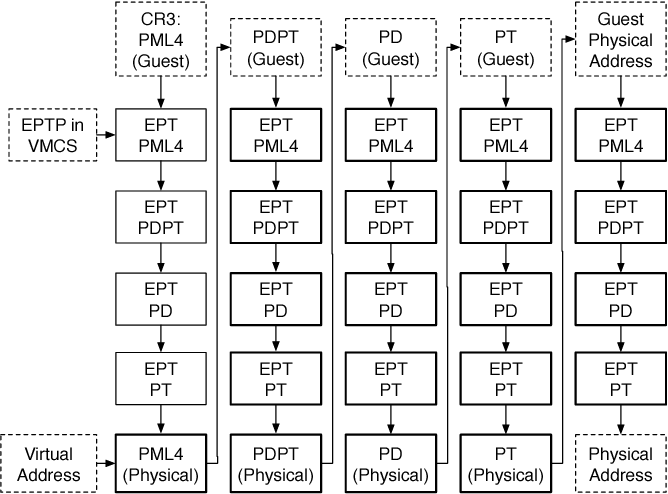
Extended Page Table (EPT, Hardware-assisted Paging)
- Reduce VM-exit calls, number of TLB flushes.
- One page table is maintained by Guest OS generate the guest physical address (GPA)
- One page table is maintained by VMM, maps the GPA to Physical Address (PA)
- When the Guest OS is executing under VMM in a new root mode (Intel VT-x VMXON) access a GVA, the Hardware MMU will walk both Guest Page Table and the Extended Page Table
EPT MMU directly gets the guest’s physical address from the guest page table and then map to the host’s physical address (doing all the hardwork within the CPU).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| // See Table 24-8. Format of Extended-Page-Table Pointer
typedef union _EPTP {
ULONG64 All;
struct {
UINT64 MemoryType : 3; // bit 2:0 (0 = Uncacheable (UC) - 6 = Write - back(WB))
UINT64 PageWalkLength : 3; // bit 5:3 (This value is 1 less than the EPT page-walk length)
UINT64 DirtyAndAceessEnabled : 1; // bit 6 (Setting this control to 1 enables accessed and dirty flags for EPT)
UINT64 Reserved1 : 5; // bit 11:7
UINT64 PML4Address : 36;
UINT64 Reserved2 : 16;
}Fields;
}EPTP, *PEPTP;
|
ETP Implementation
Hypervisor-From-Scratch\Part 4 - Address Translation Using Extended Page Table (EPT)\MyHypervisorDriver\MyHypervisorDriver\EPT.c
EPTP Dirty Flags
Setting this flag causes processor accesses to guest paging structure entries to be treated as writes.
VMRESUME & VMLAUNCH
Initializing EPT & VMX
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| __try
{
//
// Initiating EPTP and VMX
// Initialize a memory page and store instruction \xF4 on it (i.e., g_VirtualGuestMemoryAddress)
//
PEPTP EPTP = InitializeEptp();
//Initialize g_GeustState Continous memory pages to store GUest VM State, including VMCS regions and vmmstack, MSRBitmap
for (size_t i = 0; i < (100 * PAGE_SIZE) - 1; i++)
{
void * TempAsm = "\xF4";
memcpy(g_VirtualGuestMemoryAddress + i, TempAsm, 1);
}
InitiateVmx();
....
|
Setting up the EPT structure on host and initialize VMXON region & VMCS Region (physical memory)
Launch VM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| LaunchVm(ProcessorID, EPTP)
{
//Setting one processor to run
KAFFINITY AffinityMask;
AffinityMask = MathPower(2, ProcessorID);
KeSetSystemAffinityThread(AffinityMask);
// Initialize VMM Stack
UINT64 VMM_STACK_VA = ExAllocatePoolWithTag(NonPagedPool, VMM_STACK_SIZE, POOLTAG);
g_GuestState[ProcessorID].VmmStack = VMM_STACK_VA;
//Setting up MSRBitmap
g_GuestState[ProcessorID].MsrBitmap = MmAllocateNonCachedMemory(PAGE_SIZE); // should be aligned
g_GuestState[ProcessorID].MsrBitmapPhysical = VirtualToPhysicalAddress(g_GuestState[ProcessorID].MsrBitmap);
// Clear VMCS
if (!ClearVmcsState(&g_GuestState[ProcessorID]))
{
goto ErrorReturn;
}
//Load the VMCS with previous initialized g_GuestState->VmcsRegion
if (!LoadVmcs(&g_GuestState[ProcessorID]))
{
goto ErrorReturn;
}
}
|
Setup VMCS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| __vmx_vmwrite(HOST_ES_SELECTOR, GetEs() & 0xF8);
__vmx_vmwrite(HOST_CS_SELECTOR, GetCs() & 0xF8);
__vmx_vmwrite(HOST_SS_SELECTOR, GetSs() & 0xF8);
__vmx_vmwrite(HOST_DS_SELECTOR, GetDs() & 0xF8);
__vmx_vmwrite(HOST_FS_SELECTOR, GetFs() & 0xF8);
__vmx_vmwrite(HOST_GS_SELECTOR, GetGs() & 0xF8);
__vmx_vmwrite(HOST_TR_SELECTOR, GetTr() & 0xF8);
|
Saving Virtual Machine State
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| typedef struct _VIRTUAL_MACHINE_STATE
{
UINT64 VmxoRegion; // VMXON region
UINT64 VmcsRegion; // VMCS region
UINT64 Eptp; // Extended-Page-Table Pointer
UINT64 VmmStack; // Stack for VMM in VM-Exit State
UINT64 MsrBitmap; // MSR Bitmap Virtual Address
UINT64 MsrBitmapPhysical; // MSR Bitmap Physical Address
} VIRTUAL_MACHINE_STATE, *PVIRTUAL_MACHINE_STATE;
|
Saving Host Routines/Registers On Stack
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| //
// Allocate stack for the VM Exit Handler
//
UINT64 VMM_STACK_VA = ExAllocatePoolWithTag(NonPagedPool, VMM_STACK_SIZE, POOLTAG);
g_GuestState[ProcessorID].VmmStack = VMM_STACK_VA;
if (g_GuestState[ProcessorID].VmmStack == NULL)
{
DbgPrint("[*] Error in allocating VMM Stack.\n");
return;
}
RtlZeroMemory(g_GuestState[ProcessorID].VmmStack, VMM_STACK_SIZE);
|
Saving MSRBitmap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| //
// Allocate memory for MSRBitMap
//
g_GuestState[ProcessorID].MsrBitmap = MmAllocateNonCachedMemory(PAGE_SIZE); // should be aligned
if (g_GuestState[ProcessorID].MsrBitmap == NULL)
{
DbgPrint("[*] Error in allocating MSRBitMap.\n");
return;
}
RtlZeroMemory(g_GuestState[ProcessorID].MsrBitmap, PAGE_SIZE);
g_GuestState[ProcessorID].MsrBitmapPhysical = VirtualToPhysicalAddress(g_GuestState[ProcessorID].MsrBitmap);
|
Saving RSP to return from Non-root Mode
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| AsmSaveStateForVmxoff PROC PUBLIC
MOV g_StackPointerForReturning, RSP
MOV g_BasePointerForReturning, RBP
RET
AsmSaveStateForVmxoff ENDP
AsmVmxoffAndRestoreState PROC PUBLIC
VMXOFF ; turn it off before existing
MOV RSP, g_StackPointerForReturning
MOV RBP, g_BasePointerForReturning
; make rsp point to a correct return point
ADD RSP, 8
; return True
XOR RAX, RAX
MOV RAX, 1
; return section
MOV RBX, [RSP+28h+8h]
MOV RSI, [RSP+28h+10h]
ADD RSP, 020h
POP RDI
RET
AsmVmxoffAndRestoreState ENDP
|
Setting Up VMCS
A lot of the VMCS bits can cause some VM-Exits and other behaviors
Secondary Controls
PIN-Based Execution Control
Resources
Understand Full Virtualization, Paravirutalization, and Hardware Assit
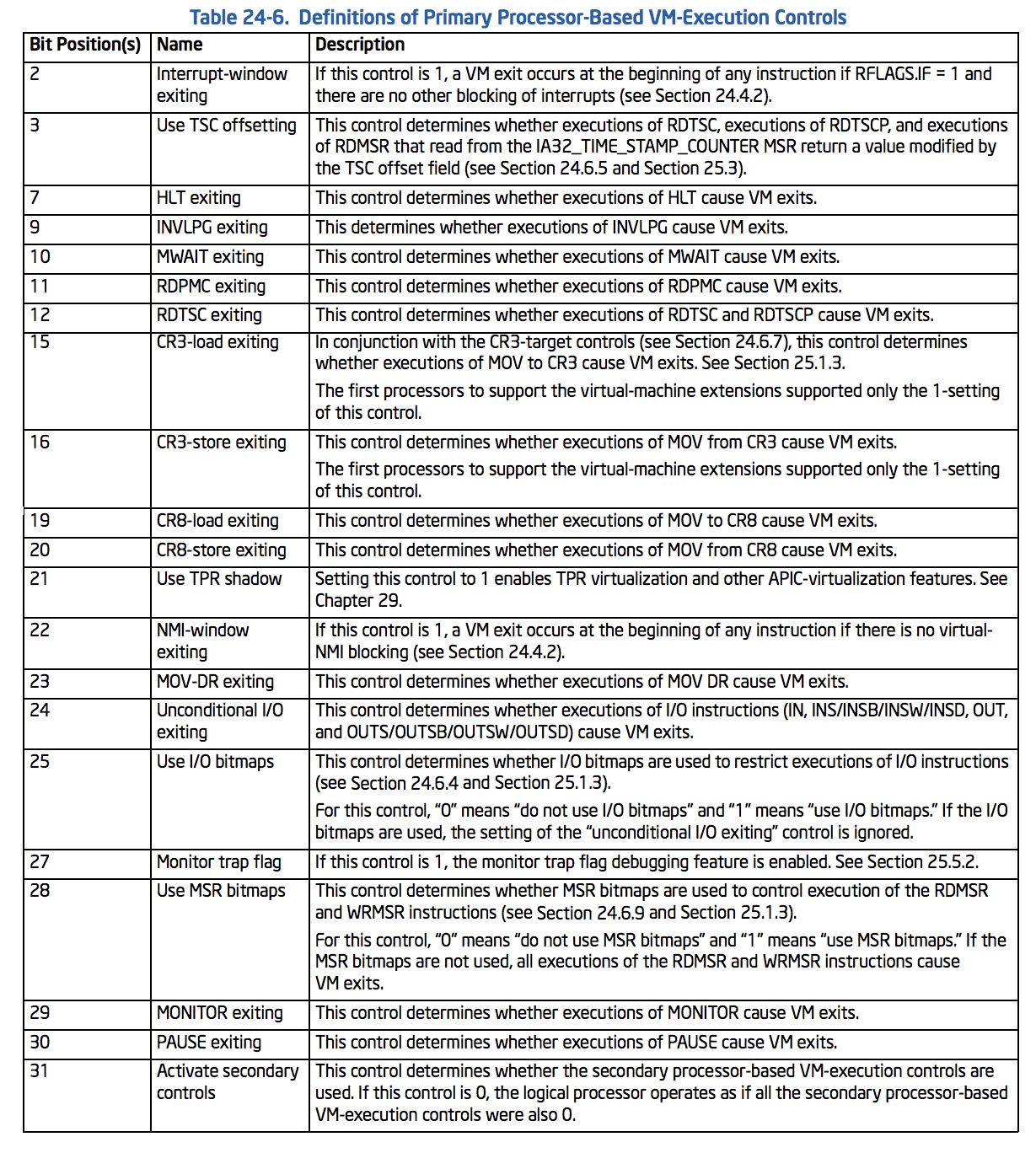 A lot of the VMCS bits can cause some VM-Exits and other behaviors
A lot of the VMCS bits can cause some VM-Exits and other behaviors